Selecting Residence Time
Since all chemical reactions are time dependent, reproducible timing of sample transport through the flow path is the critical requirement for all flow based assays.
1.2.21.
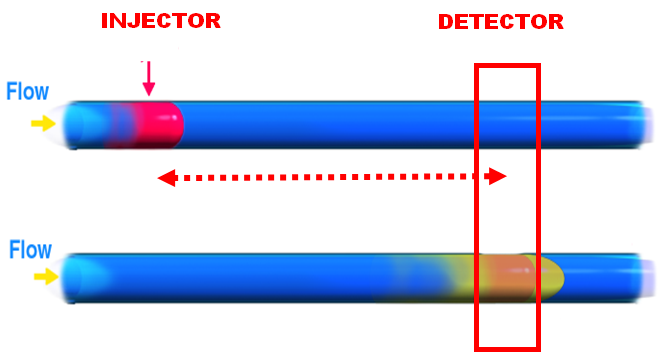
At a constant flowrate, the time interval available for a chemical reaction is defined by linear flow velocity and is limited by the length and volume of the conduit between the point of injection and the detector. Although longer tubes allow longer reaction times, the yield is offset by dilution due to an increase in sample zone dispersion.
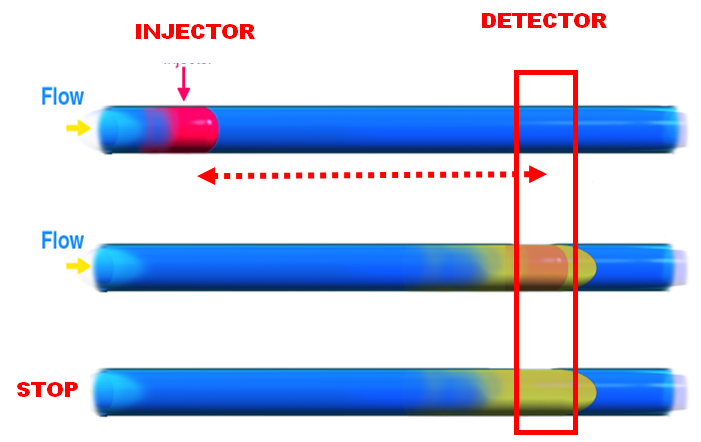
Stop flow allows a longer reaction time without penalty of dilution, thus yielding higher sensitivity. It requires less reagent and generates less waste than continuous pumping. It allows miniaturization by minimizing the length between injector and detector. It provides information on reaction kinetics through reaction rate measurements and is micro miaturized in SI lab-on-valve systems (Chapter 2).
Programmed flow, based on using different flow rates during an assay cycle. is most versatile and suited for both FI and SI.